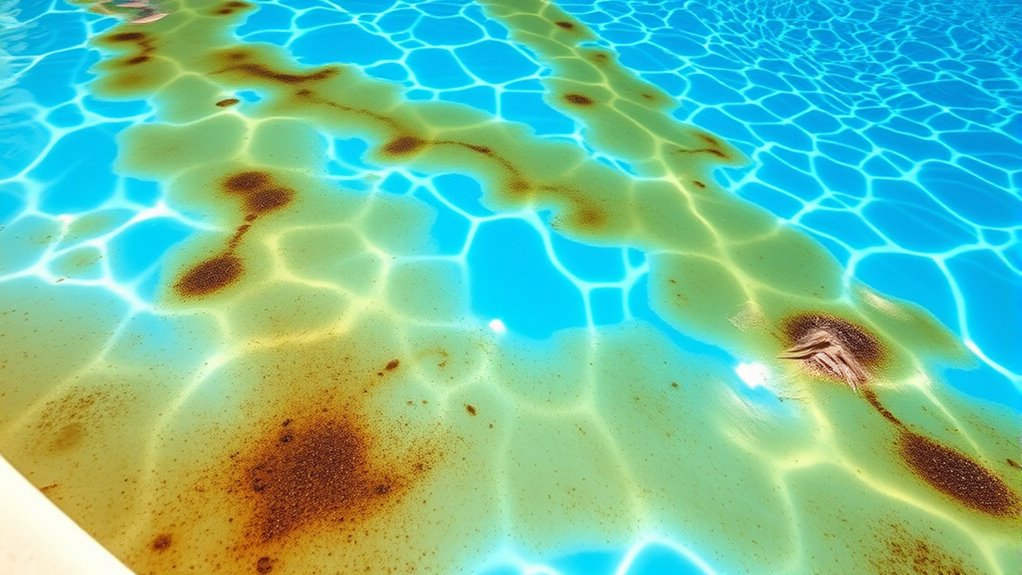
Brown stains in your pool often come from metal contaminants like iron, copper, or manganese entering through corroding pipes, well water, or aging equipment. These metals can stain pool surfaces when water chemistry isn’t balanced, especially with low pH or high chlorine levels. Regular testing, proper maintenance, and using metal sequestrants can prevent future stains. To keep your pool clear and stain-free, understanding these causes and solutions is essential—if you keep exploring, you’ll discover simple ways to protect your pool.
Key Takeaways
- Brown stains often result from iron leaching due to corrosion or high iron levels in source water.
- Low pH and high sanitizer levels accelerate metal corrosion, causing metal particles to stain pool surfaces.
- Metal-based algaecides and chemicals can introduce or increase metal content, leading to staining.
- Regular testing and maintaining proper water chemistry prevent metal leaching and staining.
- Using metal sequestrants and corrosion-resistant equipment helps prevent brown stains caused by metal buildup.
Common Causes of Metal Stains in Pools
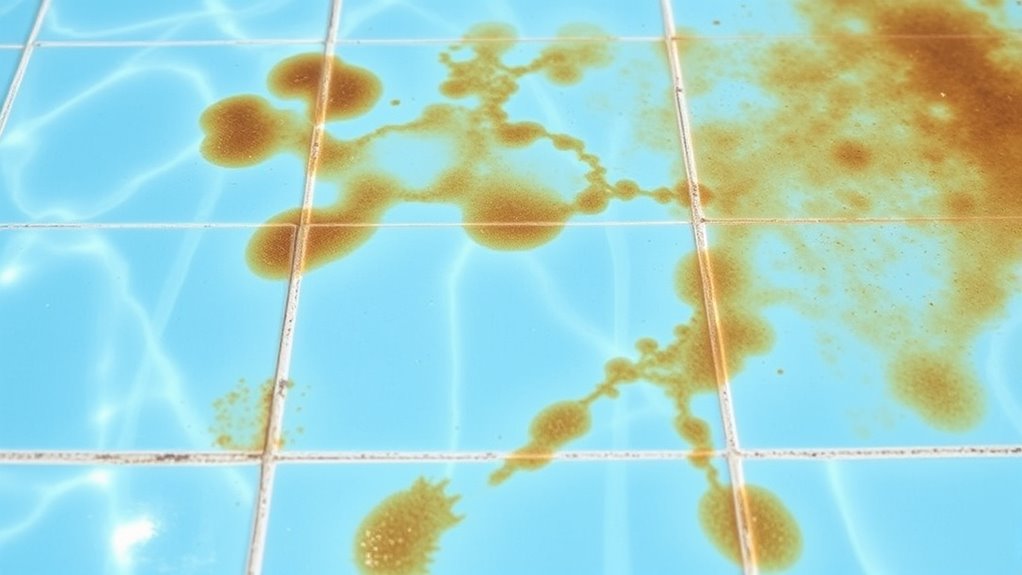
Have you ever noticed brown or rust-colored stains forming on your pool’s walls or floor? These stains often come from metals like iron, copper, or manganese, which can enter your pool through various sources. One common cause is the use of well water that contains high metal levels, especially if you haven’t tested or treated it. Additionally, aging pool equipment, such as corroding pipes or filters, can release metals into the water. Sometimes, metal particles are introduced through contaminated pool toys or algae treatments containing metal-based chemicals. Ultimately, high mineral content in your water or runoff from nearby soil can also contribute to metal deposits settling and staining your pool surfaces. Recognizing these sources helps you take steps to prevent staining before it happens. Furthermore, understanding creative practice can inspire innovative solutions for water treatment and maintenance challenges, helping you develop more effective prevention strategies.
How Metals Enter Your Pool Water
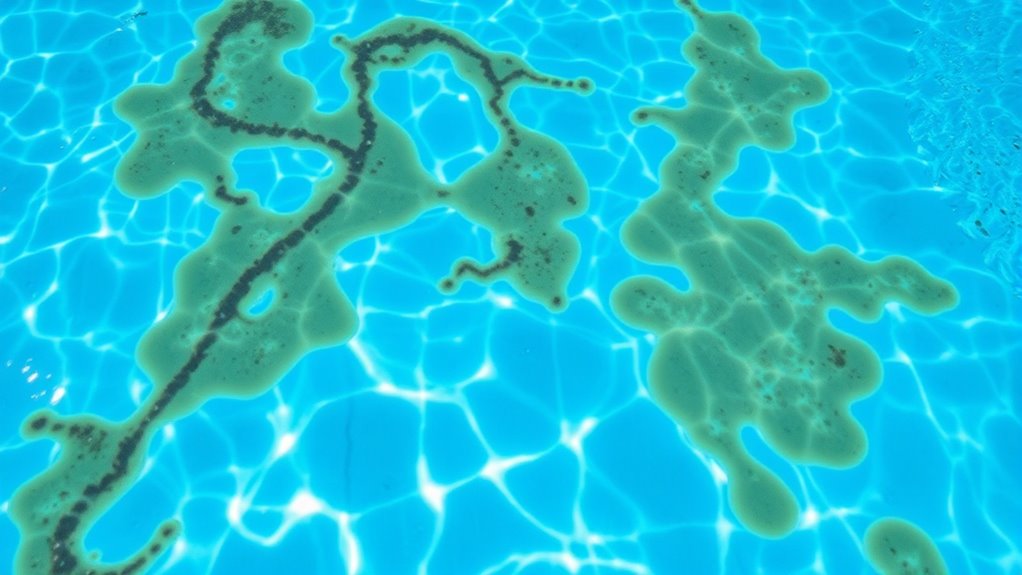
Metals can enter your pool water through various sources like corroding pipes, outdoor debris, or contaminated source water. Common metal contaminants include iron, copper, and manganese, which can cause stains and discoloration. To prevent metal entry, you should regularly test your water and use metal sequestrants or filters designed to block these contaminants. Additionally, understanding the effects of metal buildup can help you better maintain a clear, attractive pool quality.
Sources of Metal Leaching
Many common sources contribute to metals leaching into your pool water, often without you realizing it. One major source is corroding plumbing fixtures or pipes, which release metals like iron and copper into the water. Additionally, source water itself may contain metals, especially if it’s drawn from wells or untreated sources. Pool equipment, such as heaters and chlorinators, can also corrode over time, releasing metals into the water. Metal-based algaecides and certain shock treatments are another culprit, adding metals directly when used improperly. Ultimately, debris from nearby rusted fences or metal structures can introduce metals, especially during storms or high winds. Being aware of these sources helps you prevent unwanted metal buildup, keeping your pool clear and preventing stains.
Common Metal Contaminants
Understanding how metals enter your pool water is key to managing contamination. The most common metal contaminants are iron, copper, and manganese. Iron often comes from corroded pipes, well water, or nearby rusting structures. Copper typically leaches from old plumbing, pool equipment, or algaecides containing copper compounds. Manganese, though less common, can enter through well water or natural sources in the environment. These metals can dissolve into your water, especially when pH levels are unbalanced or oxidizing agents are used excessively. Once in the water, they can cause brown, green, or black staining on pool surfaces and equipment. Recognizing these common contaminants helps you identify their sources and take steps to minimize their presence, reducing the risk of unsightly stains and damage. Proper water testing and metal contamination prevention measures are essential for maintaining a clear and healthy pool.
Prevention of Metal Entry
How can you prevent metals from entering your pool water? Start by testing your source water regularly, especially if you use well water or water from a nearby river or lake. If metals are present, consider installing a pre-filter or using a water filtration system designed to remove heavy metals before it reaches your pool. Keep your pool’s pH and alkalinity balanced; unstable water chemistry can cause metals to leach from pipes and fixtures. Avoid using metal-based algaecides or chlorine products containing metals. Additionally, promptly address any leaks or corrosion in your pool equipment, as these can introduce metals into the water. Regular maintenance and vigilant water testing are your best defenses against unwanted metal entry, helping keep your pool clean and free of stains. Utilizing a whole-house water filtration system can provide comprehensive protection against metals and other contaminants entering your water supply.
Recognizing the Signs of Metal Stains
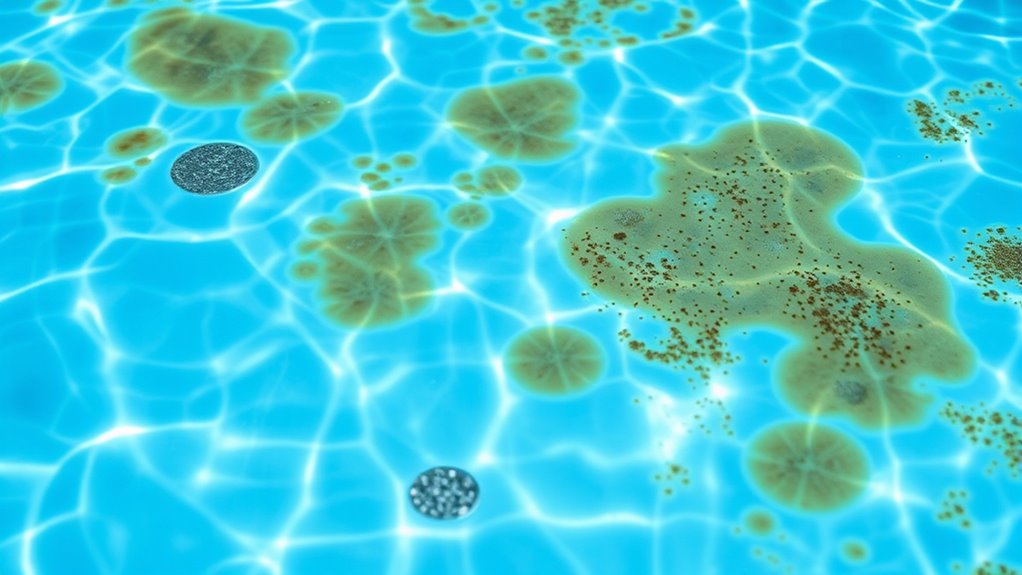
You might notice unusual discoloration patterns on your pool’s surfaces or a strange tint in the water. These signs often indicate metal stains caused by metals present in the water. Recognizing these visual clues early can help you address the problem before it worsens. Using water testing kits can help identify metal concentrations and determine the cause of staining.
Visible Discoloration Patterns
Metal stains in pools often reveal themselves through distinctive discoloration patterns that are easy to spot once you know what to look for. You might notice brown or rust-colored streaks along the pool walls or floor, often appearing as irregular patches or streaks. These stains tend to form near metal fixtures, drains, or areas with high water flow. Sometimes, they look like blotches or ring-shaped spots, especially around the waterline. If you see these patterns, it’s a clear sign that metals like iron or copper are reacting with pool chemicals or water chemistry. Recognizing these visual cues early helps you address the issue before stains become more stubborn or widespread, saving you time and effort in stain removal. Additionally, understanding the importance of proper water chemistry can help prevent future metal stains from forming.
Unusual Water Tint
Have you noticed a strange tint in your pool water? This unusual coloring often signals underlying metal issues. A slight green or brownish hue can indicate the presence of copper or iron, respectively. Unlike visible stains, these tints are subtle and may only be noticeable in certain lighting or angles, making them easy to overlook. If your water looks cloudy or takes on an odd color, it’s time to investigate further. Metal particles suspended in the water can cause these tints, especially if your pool chemistry is out of balance or if water sources contain metals. Recognizing these signs early helps prevent staining and damage. Regular testing and monitoring your water’s color can alert you to potential metal contamination before it becomes a bigger problem.
The Role of Water Chemistry in Metal Staining
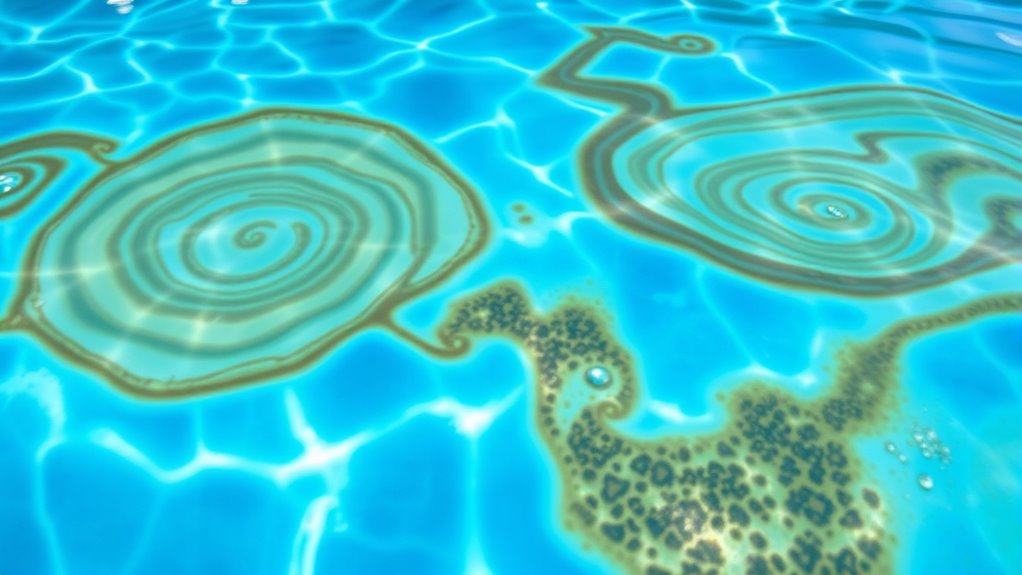

Water chemistry plays a crucial role in the formation of metal stains in pools. When the pH level is too low or high, it can cause metals like iron and copper to become more soluble, increasing the risk of staining. High levels of total dissolved solids (TDS) or improper alkalinity can also accelerate metal oxidation, leading to stubborn brown or green stains. Chlorine and other sanitizers, if not properly balanced, can further contribute to metal corrosion, releasing metals into the water. Additionally, using untreated or contaminated source water introduces metals directly into your pool. Keeping your water chemistry balanced—monitoring pH, alkalinity, and sanitizer levels—helps prevent metal ions from precipitating and staining your pool surfaces. Understanding metal solubility is key to managing and preventing stains. Proper water management is essential for maintaining a stain-free pool.
Effects of Pool Equipment and Corrosion

Your pool equipment can contribute to metal stains when corrosion causes metal parts to leach into the water. The materials used in your equipment influence how quickly this happens, so choosing resistant options helps. Regular maintenance and inspections are key to preventing corrosion and keeping your pool clean. Additionally, understanding vibrational energy can help you maintain a positive mindset about your pool’s condition and potential solutions.
Corrosion Causes Metal Leaching
Corrosion of pool equipment often leads to metal leaching into the water, causing stains and potential damage. When metal parts like ladders, filters, or heaters corrode, tiny particles break off and dissolve into the pool water. This process accelerates if the water’s pH is too low or if the water contains high levels of chlorine or other chemicals. As metals such as iron, copper, or manganese leach into the water, they can create brown, green, or black stains on the pool surfaces. The leached metals also pose risks to swimmers and can damage equipment over time. To minimize leaching, you need to regularly inspect your equipment for signs of corrosion and maintain proper water chemistry. Doing so helps prevent metal stains and prolongs the lifespan of your pool equipment.
Equipment Material Effects
Different materials used in pool equipment can markedly influence how quickly corrosion occurs and how metal stains develop. For example, metal components made from stainless steel resist corrosion better than softer metals like copper or brass, reducing stain formation. Aluminum parts may corrode faster in high-chlorine environments, releasing aluminum ions that can stain your pool’s surface. Additionally, certain pool fixtures, such as fittings or ladders, made from incompatible metals can create galvanic reactions when in contact with pool water, accelerating corrosion. The use of non-metallic or coated equipment can slow down these processes. Selecting equipment crafted from corrosion-resistant materials and avoiding direct contact between incompatible metals can notably reduce staining risks and prolong the lifespan of your pool’s interior. Moreover, using corrosion-resistant materials in pool equipment can significantly enhance longevity and maintain a cleaner pool environment.
Preventative Maintenance Strategies
Implementing regular preventative maintenance is essential to minimize the effects of equipment-related corrosion and metal staining in your pool. By inspecting and cleaning your equipment, you prevent rust buildup that can leach metals into your water. Using corrosion-resistant materials and ensuring proper water chemistry also helps protect your equipment from deterioration. Additionally, replacing outdated or damaged parts promptly reduces the risk of metal leaching. Staying informed about trailer music composition techniques can help you create more engaging soundtracks that set the right mood. Here’s a quick overview:
| Maintenance Strategy | Benefits |
|---|---|
| Regular Inspection | Detects early signs of corrosion |
| Water Chemistry Checks | Maintains balanced pH and alkalinity |
| Equipment Upgrades | Reduces risk of metal leaching and stains |
Stay proactive to keep your pool clean, clear, and free of unsightly stains.
Preventative Measures to Keep Metals Out of Your Pool

To keep metals out of your pool, taking proactive steps before problems arise is essential. First, use a metal sequestrant regularly to bind with metals and prevent them from settling or staining. Check your source water for high metal content before filling your pool, and consider installing a pre-filter or using a water treatment system to remove metals. Maintain proper water chemistry, especially pH and alkalinity levels, to reduce corrosion and metal leaching from pool equipment. Avoid using metal-based algaecides or other chemicals that can introduce metals into the water. Regularly clean your filter and pool surfaces to prevent metal buildup. By staying vigilant and implementing these measures, you can appreciably reduce the risk of metal stains and keep your pool looking clear and beautiful.
Testing and Monitoring Your Pool Water
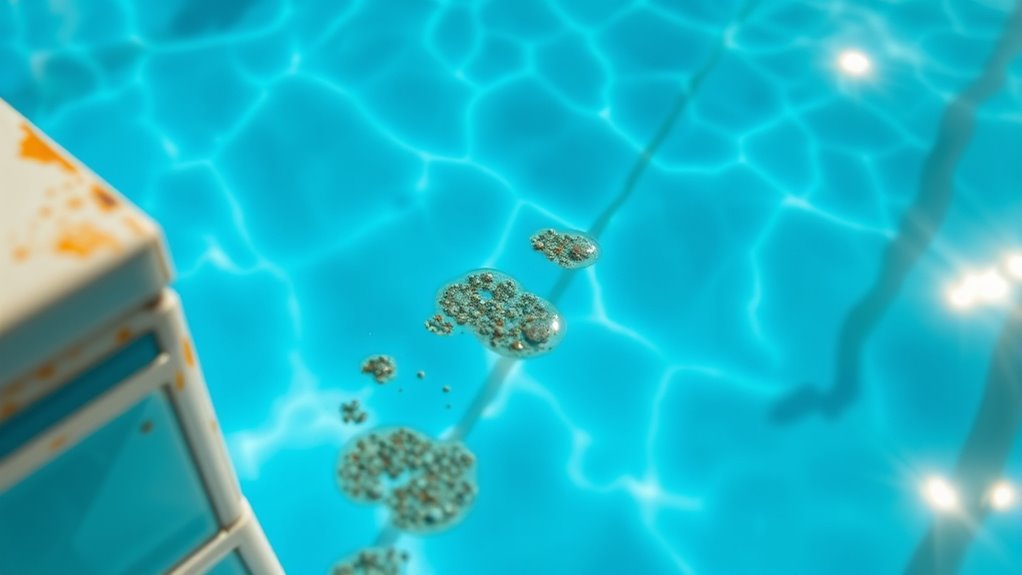
Regularly testing and monitoring your pool water is essential to catch metal issues early and maintain ideal water quality. Use test strips or a digital tester to check levels of metals like iron and copper at least once a week, especially after storms or heavy rainfall. Keep an eye on pH, alkalinity, and sanitizer levels, as imbalances can cause metals to oxidize and stain your pool. Record your readings to identify patterns and detect rising metal concentrations before they cause stains. If your tests show elevated metal levels, consider using metal sequestrants or other treatments promptly. Consistent monitoring helps you catch problems early, preventing brown or green staining and prolonging your pool’s clarity and cleanliness.
Effective Treatments for Existing Metal Stains
When metal stains have already appeared in your pool, prompt treatment is key to restoring its clarity. Start by lowering your pool’s pH to around 7.0, which helps metals stay in solution. Use a metal sequestrant or chelating agent, following the manufacturer’s instructions, to bind with the metals and prevent further staining. You may need to add a stain remover specifically formulated for metal stains; these often contain EDTA or similar agents. Run your pool filter continuously to circulate the chemicals. For stubborn stains, brushing the affected areas can help loosen deposits. In severe cases, professional pool draining and acid washing might be necessary. Always follow safety precautions and consult product labels for proper application.
Best Practices for Pool Maintenance and Care

Maintaining a clean and balanced pool requires consistent attention to water chemistry, filtration, and overall upkeep. Regularly test your water’s pH, alkalinity, and chlorine levels to prevent imbalances that can cause staining. Keep your filtration system clean and running efficiently to remove debris and metals that can settle and stain your pool surface. Shock the pool weekly to eliminate contaminants and prevent metal buildup. Use metal sequestrants as a preventive measure, especially if your water source has high metal content. Brush the pool walls and floor regularly to remove deposits before they stain. Maintain proper circulation to evenly distribute chemicals and prevent localized staining. Consistent care not only keeps your pool inviting but also minimizes the risk of discoloration and staining over time.
Long-Term Strategies to Prevent Future Staining

Implementing long-term strategies is key to keeping your pool free from future staining. Regularly test and balance your water chemistry, especially pH and alkalinity levels, to prevent metal buildup that causes stains. Use a metal sequestrant regularly, as it binds metals and keeps them in solution, reducing stain risk. Consider installing a water filtration system that effectively removes metals before they enter your pool. Maintain consistent water circulation and filtration to prevent mineral deposits from settling. Also, monitor your source water for high metal content and treat it accordingly. Scheduling routine inspections and cleanings helps catch potential issues early. By staying proactive and diligent, you’ll considerably lower the chances of future metal stains, keeping your pool clean, clear, and beautiful year-round.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can Metal Stains Be Harmful to Swimmers’ Health?
Metal stains in your pool are generally not harmful to swimmers’ health. They’re caused by metals like iron or copper, which can come from water sources or pool equipment. While the stains themselves aren’t dangerous, swimming in water with high metal concentrations isn’t recommended. To stay safe, maintain proper water chemistry and consider testing your water regularly. If needed, use metal removers to reduce metal levels and prevent staining.
Are Certain Types of Pool Filters Better at Preventing Metal Buildup?
Yes, certain pool filters are better at preventing metal buildup. You should opt for high-quality sand or cartridge filters designed to trap tiny metal particles effectively. Regularly cleaning and backwashing your filter ensures it functions efficiently, reducing metal accumulation. Don’t overlook the importance of water testing and balancing, as proper chemical levels help prevent metals from leaching into your pool, keeping it clear and stain-free.
How Do Mineral Levels in Well Water Affect Metal Staining?
Mineral levels in your well water directly impact metal staining in your pool. High levels of minerals like iron and manganese can cause brown or rust-colored stains when they oxidize. To prevent this, you should regularly test your well water and use water treatment systems like filtration or water softeners to reduce mineral concentrations. Maintaining proper chemical balance and using metal sequestrants also helps minimize staining caused by mineral content.
Can Using Metal Sequestrants Cause Any Long-Term Damage?
Think of metal sequestrants as a shield for your pool, but if overused, they can cause long-term buildup that’s like a stubborn layer of grime. While they’re generally safe when used correctly, excessive use might lead to cloudy water or interfere with sanitizer effectiveness. Always follow dosing instructions, and don’t overdo it, to keep your pool sparkling without risking damage from too much of a good thing.
What Are the Environmental Impacts of Chemical Treatments for Metal Stains?
Chemical treatments for metal stains can impact the environment by introducing potentially harmful substances into water systems. You might notice chemicals like sequestrants or chelating agents entering local waterways through runoff or backwashing. To minimize this, you should use treatments sparingly and follow manufacturer instructions closely. Proper disposal of excess chemicals and avoiding overuse helps reduce environmental harm, protecting aquatic life and water quality in your community.
Conclusion
So, next time your pool turns a lovely shade of rust, just remember—it’s not a mystery from the deep. With a little attention and some basic upkeep, you can keep that pool sparkling instead of resembling a backyard brew of iron and dirt. Because who wouldn’t want a crystal-clear oasis, not a muddy mess? Stay vigilant, test often, and you’ll be swimming in clarity, not chaos—no magic required.









